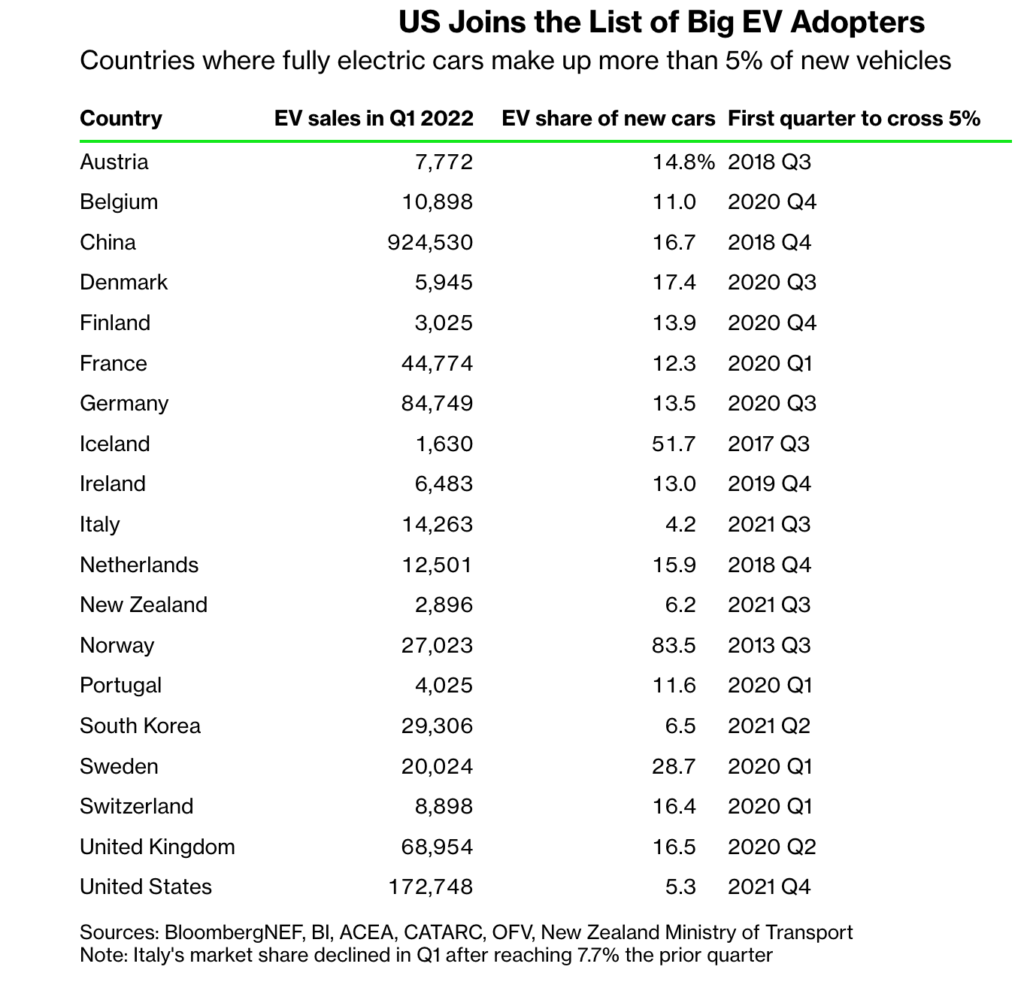
According to a recent Bloomberg report, the “US is the latest country to pass what’s become a critical EV tipping point: 5% of new car sales powered only by electricity.”
That 5% threshold is significant because it seems to be the point at which early adopters are overtaken by majority and rapid acceleration in demand occurs. The US joins a list of 19 other countries that have reached this 5% threshold and, if following a similar trend, will achieve 25% of new cars being fully electric in 2025.
Charging Infrastructure
The increase in electric vehicles on the road is, unsurprisingly, resulting in an increased demand for charging infrastructure. Public and private networks are being installed at a rapid pace and that will continue to increase as more public funding becomes allocated to charging infrastructure.
EV drivers expect charge points to be available for use when they need them and governments are looking for ways to address reliability concerns. The US Department of Transportation is proposing new standards which aim to make charging EVs convenient, reliable, and affordable for all Americans. In the UK, where approximately 600 public stations are installed per month, the Department for Transport recently announced plans to require a 99% reliability rate for rapid stations. For charge point operators, lack of reliability affects their business as downtime can mean loss of revenue and a negative customer experience.
Secure connectivity at charge points sites is a prerequisite for collecting data from equipment, people, and the environment. Data collected can provide meaningful insights on customer behavior that can help improve business processes and enhance customer experience. That’s why connectivity infrastructure forms the backbone of the EV charge point network.
Types of Connectivity
There are numerous ways to connect EV charge points, ranging from simple connectivity using built-in cellular modems (installed at the factory by the charge point manufacturer) to dedicated industrial gateways serving multiple charge points as well as industrial routers supporting multiple backhaul connections (DSL, fiber, cellular) and industrial switches for connecting increased numbers of EV charge points at a single location.
A solution is required that provides the flexibility to meet current needs while facilitating a clear path forward as complexity and scale evolve. Cisco’s validated solutions support these needs, providing the following key benefits and more:
- Flexible deployment options: Support simple to advanced solutions that cover various deployment options.
- Simplified provisioning: Enable simple onboarding, monitoring, and management of the remote equipment.
- Simplified operations: Increase operational visibility, minimize outages, and enable faster remote issue resolution.
- Multilevel security: Provide end-to-end robust security capabilities (physical and cyber) to protect the charging infrastructure and associated services
Cisco Connectivity Solutions
Today, Cisco’s connectivity solution provides for management and monitoring of connected EV charge points, video surveillance and monitoring, vehicle and pedestrian safety monitoring, secure remote access, digital signage, and data offload.

Data can unlock new value in terms of business and operating models. Charge point operators can apply technology to connect, collect, transform, and analyze data from their network of stations. As these networks continue to grow and evolve, advanced use cases for retailers, fleet operators, utilities, and automotive OEMs will emerge.
At Cisco, we believe in powering an inclusive future for all by bringing communities together and creating meaningful change for everyone, including our planet. As the world builds the future of sustainable, electrified transportation, robust networking infrastructure that is simple to deploy, manage, and operate is becoming essential. Cisco’s connectivity solutions provide the ability to address this at scale in a rapidly growing market.
This article was originally published by Cisco.