On Q: Using Data to Improve Work Zone Safety
In honor of National Work Zone Awareness Week, we shed some light on the growing importance of shareable work zone data and automated lane closure management.
NWZAW is an annual spring campaign held at the start of construction season to encourage safe driving through highway work zones in the US.
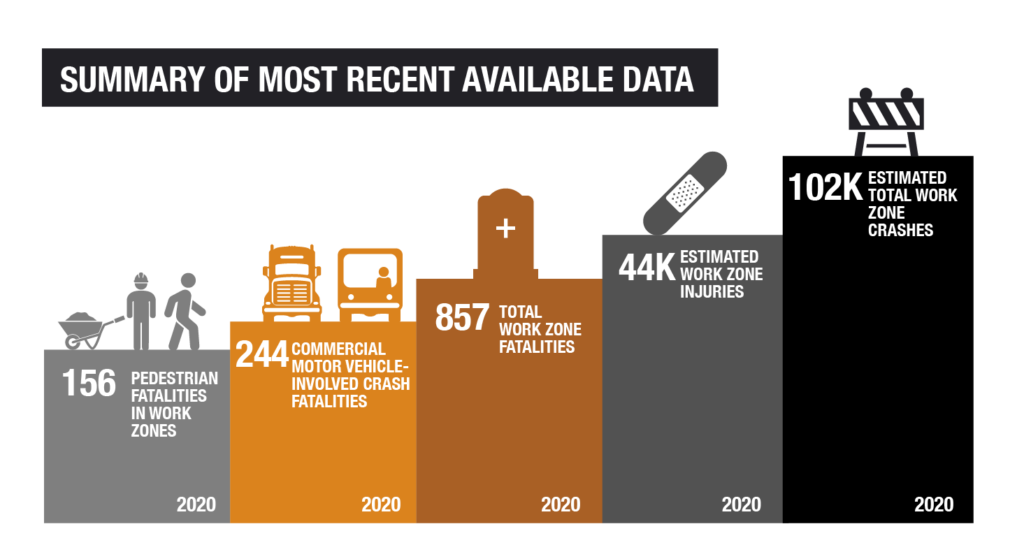
Whether for temporary maintenance or an extended amount of time for construction, work zones are an essential piece of maintaining and upgrading our roadways. Yet, they present dangers for workers, motorists, and pedestrians alike – as seen below.
Managing work zones present numerous challenges to agencies, such as:
- Worker, motorist, and pedestrian safety
- Congestion, delays, and incident management
- Roadway capacity, speed reductions, awareness, and visibility
- Detours and alternate route availability
- Coordination among multiple stakeholders/agencies/departments/regions
- Sharing work zone data information
Thankfully, there are many tools available to help agencies mitigate risks without compromising safety and mobility. One such step is to centrally coordinate, manage, and share work zone activities and data.
For most, data on work zone activities and related lane closures is ad-hoc, manual, and limited in scope – making work zone data challenging to manage and practically impossible to share.
This siloed nature, in conjunction with changing traffic patterns and narrowed roadways, creates a deadly combination of events that cause congestion and pollution, create driver and worker stress, and claim lives every day.
Collecting data on the location, time, and impact of work zones in a standardized, distributable format is key to improving work zone safety and the purpose of the Work Zone Data Exchange.
Introducing the Work Zone Data Exchange
The Work Zone Data Exchange (WZDx) aims to create standardized data definitions to facilitate ubiquitous access to work zone data, particularly by connected and autonomous vehicles (CAVs), for improved road and worker safety.
In addition to CAVs, this data would benefit:
- Neighboring jurisdictions and regions
- Law enforcement and emergency service providers
- Traveler information systems
To pilot the specification, raise awareness, and (hopefully) encourage and facilitate adoption of the standard, the USDOT awarded $2.4 million in WZDx demonstration grants to fund projects in 13 states.
While still under wraps, we’re proud to report that we’ve been in talks with some grant recipients looking to leverage our tools in the accordance with the WZDx specification. Stay tuned for more information.
Gathering Work Zone Data
Sharing work zone data in a standardized format is necessary to improve work zone operations and safety. But as previously alluded to, all-too-often agencies do not have a sophisticated, yet easy to use, automated system for managing lane closures in the first place… so where will the data on work zone activities come from?
The answer could be your ATMS, smart work zone system, or integration with an automated lane closure management system, such as Q-Free’s LaneAware lane closure management tool.
LaneAware is a sophisticated web-based tool that allows approved workers and contractors to request lane closure activities. Each request is automatically checked against user-defined business rules before being approved or flagged for further review. LaneAware also helps fulfill the need of “how” work zones will impact data when integrated with an ATMS, further supporting a work zone data feed.
Road and lane closures are an unavoidable aspect of building and maintaining road infrastructure. Efficient work zone management makes planning and implementing lane closures easier and more predictable for everyone.
An integrated, automated lane closure management tool allows agencies to:
- Coordinate ongoing road works and major projects with ease
- Share work zone data with the public and media
- Minimize errors and disruption to the commuting public
By providing a means to verify and compare multiple lane closures against well-defined policies and business practices, LaneAware helps to:
- Reduce the chance for duplicate requests
- Avoid conflicting project road closures
- Remove the potential of human error in scheduling
- Compile all lane closure data in one central database
- Minimize the impact to travelers
To boot, LaneAware alleviates the time and cost associated with manually tracking work events. And it allows agencies to share lane closure data with key stakeholders and the motoring public.
This article was originally published by Q-Free ASA.















