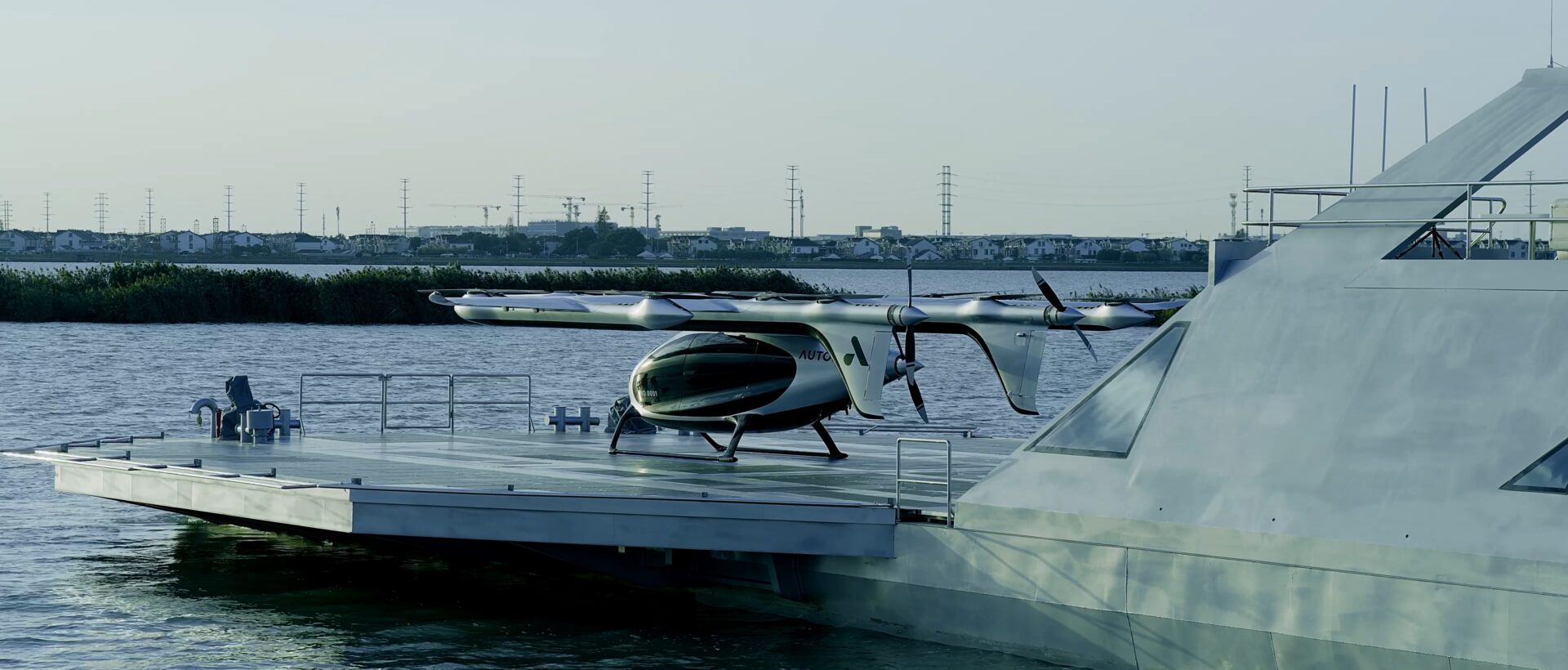
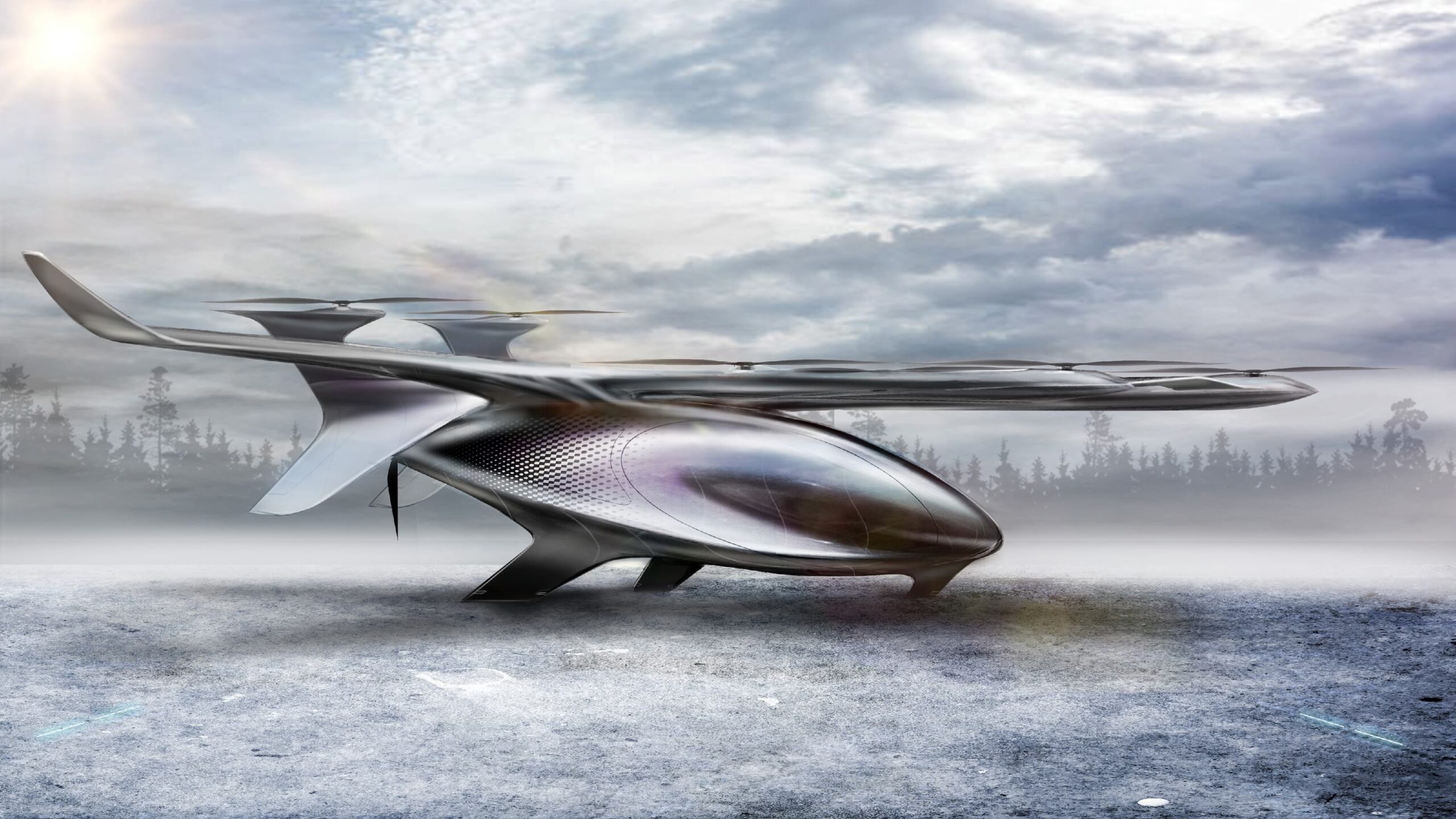
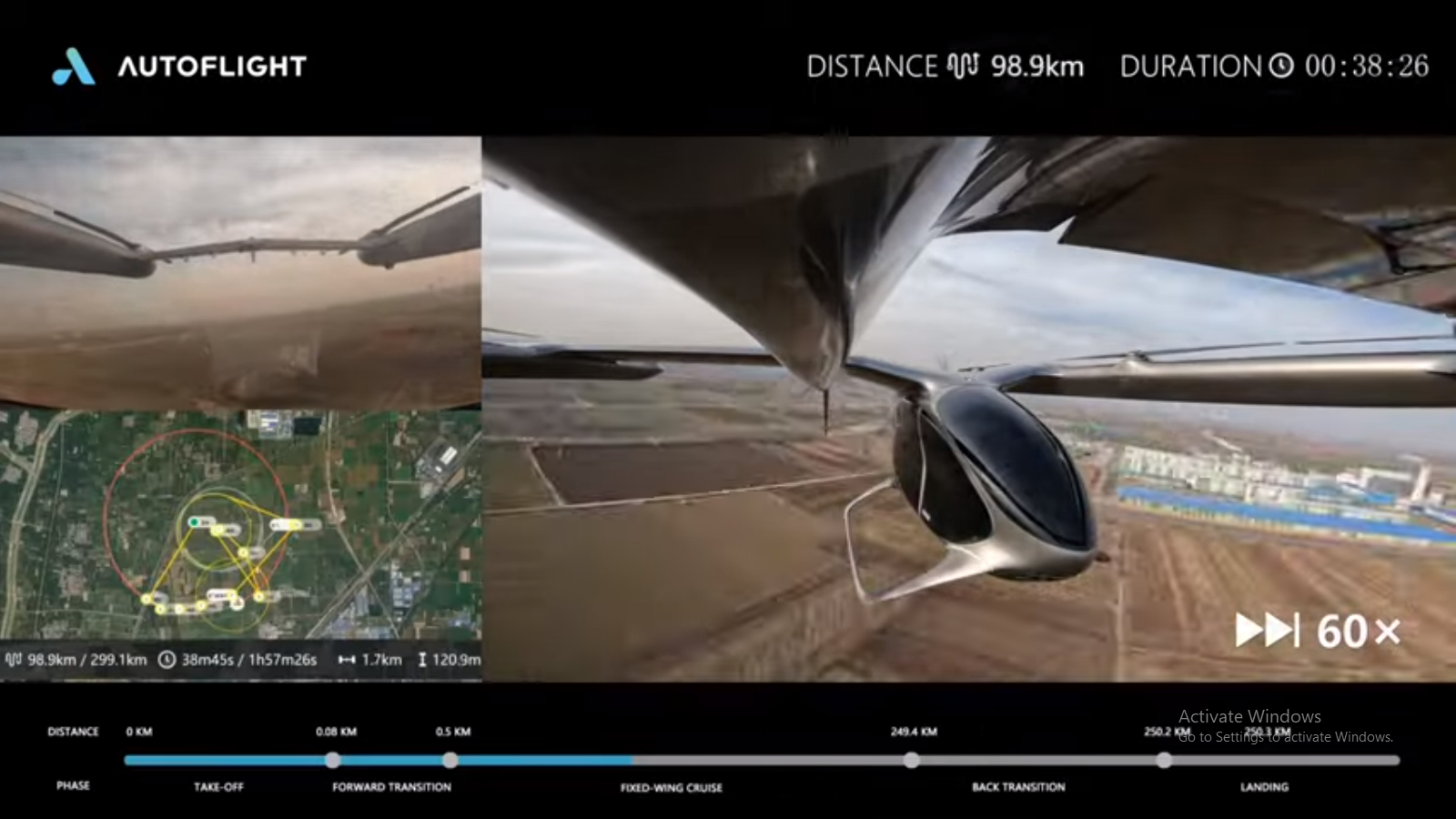
AutoFlight has introduced Matrix, a 5-ton class electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft, which has completed a public full transition flight demonstration at the company’s low-altitude flight test facility.
During the demonstration, Matrix flew alongside AutoFlight’s 2-ton CarryAll cargo eVTOL and successfully performed a full mode transition sequence, moving from vertical take-off through cruise flight to vertical landing. The flight demonstrated AutoFlight’s systems for aerodynamics, electric propulsion, and flight control on an aircraft of this size.
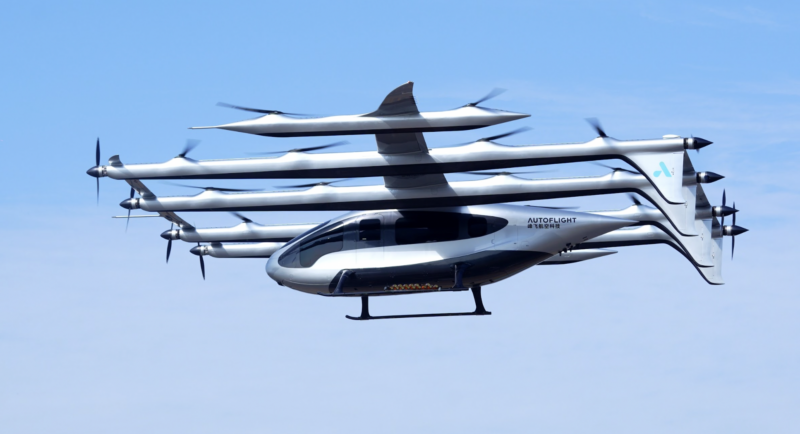

Matrix has a wingspan of 20 metres, a length of 17.1 metres, and a height of 3.3 metres, with a maximum take-off weight of 5,700kg. The cabin measures 5.25 metres in length, 1.8 metres in width, and 1.85 metres in aisle height, providing 13.9m³ of internal space.
The aircraft will be offered in passenger and cargo versions. The passenger variant can seat either 10 business-class passengers or six VIP passengers. Features include climate control, washbasins, lavatories, ambient lighting, and windows measuring 1m² with increased light transmission.
The cargo variant is equipped with a hybrid power system and can carry a maximum payload of 1,500kg. It includes a forward-opening door designed to accommodate two AKE standard air cargo containers, enabling larger-scale transport operations.
The all-electric version has an estimated range of 250 kilometres, while the hybrid-electric variant can operate up to 1,500 kilometres. The platform is intended for applications including regional travel, heavy logistics, and emergency response missions.
AutoFlight’s CEO and Founder, Tian Yu said:Matrix is not only a rising star in the aviation industry but also an ambitious industry disruptor. It will break the industry perception that eVTOL = short-haul, low-load, and will reshape the rules of eVTOL routes. Through economies of scale, it significantly reduces transportation costs per seat-kilometre and ton-kilometre, revolutionising costs and embracing profitability. It covers all scenarios from urban commuting to intercity feeder routes, driving the expansion of the entire low-altitude ecosystem.